
(for example, UML Safety Analysis Profile, UML Security Analysis Profile)
AGILE IBM SOUSCHEF UPDATE

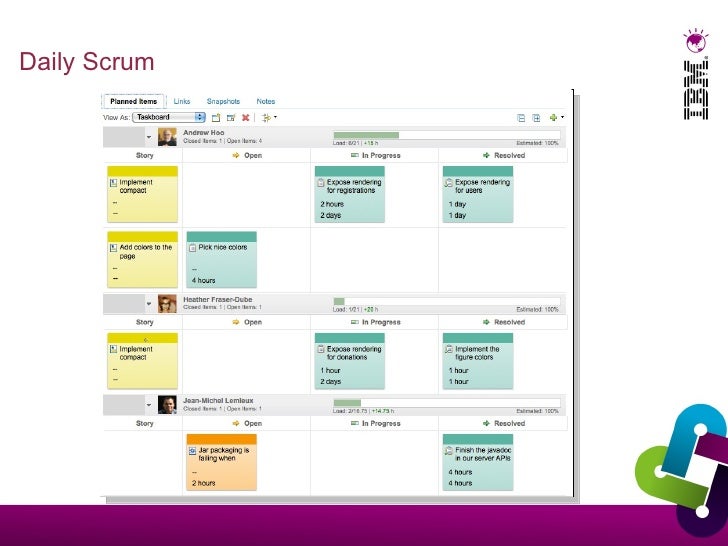
AGILE IBM SOUSCHEF VERIFICATION
Perform verification and validation at the end of each microcycle.Build the system in 4 to 6-week microcycles.Use shared interface libraries (models) for cross-component interfaces and data types Use daily integrations to ensure different developers’ implementations work together.Developers’ components don’t work together properly.Use model-based testing tooling to create test architectures and execute and analyze.Use 20 to 60-minute nanocycles for model-code-unit test cycles.Generate deployed code from models, when possible.UUse model-code associativity to synchronize models and code automatically.Execute and debug models at the model level.Architectural views are not reflected in the code.Code does not accurately reflect design.Design is not understood by relevant stakeholders.Manage schedules at the project and microcycle levels Use ERNIE estimation† to improve estimation quality Update schedules frequently founded on outcome-based metrics Use BERT scheduling* to get initial best scheduleĬreate three schedules (Best, Customer and Goal).Schedules don’t increase in accuracy during the project Schedules don’t reflect changing project needs or conditions
Handoff process migrates logical systems engineering work products to physical specifications without loss of fidelity Use principled systems engineering model organization to
AGILE IBM SOUSCHEF SOFTWARE
Loss of fidelity of information during handoff to software team

Model-based handoff from systems engineering Build state-based use case models that demonstrate the interaction of requirements by way of execution


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
